FANUC Robotics is the world’s leading manufacturer of industrial robots, known for its innovative automation solutions and signature yellow robots. Founded in 1956 in Japan by Dr. Seiuemon Inaba, FANUC began with the development of numerically controlled machines and has since expanded into a global powerhouse in robotic automation. This article explores the multifaceted aspects of FANUC Robotics, addressing its usage, finance, capabilities, history, and more.
What is FANUC Used For?
FANUC robots are used for a variety of applications in numerous industries, primarily focusing on automating manufacturing processes. These robots enhance productivity, improve product quality, reduce cycle times, and increase overall efficiency in production lines. FANUC robots can perform tasks such as welding, assembly, packaging, material removal, part transfer, inspection, machine tending, palletizing, painting, and dispensing.
What is the History of FANUC Robotics?
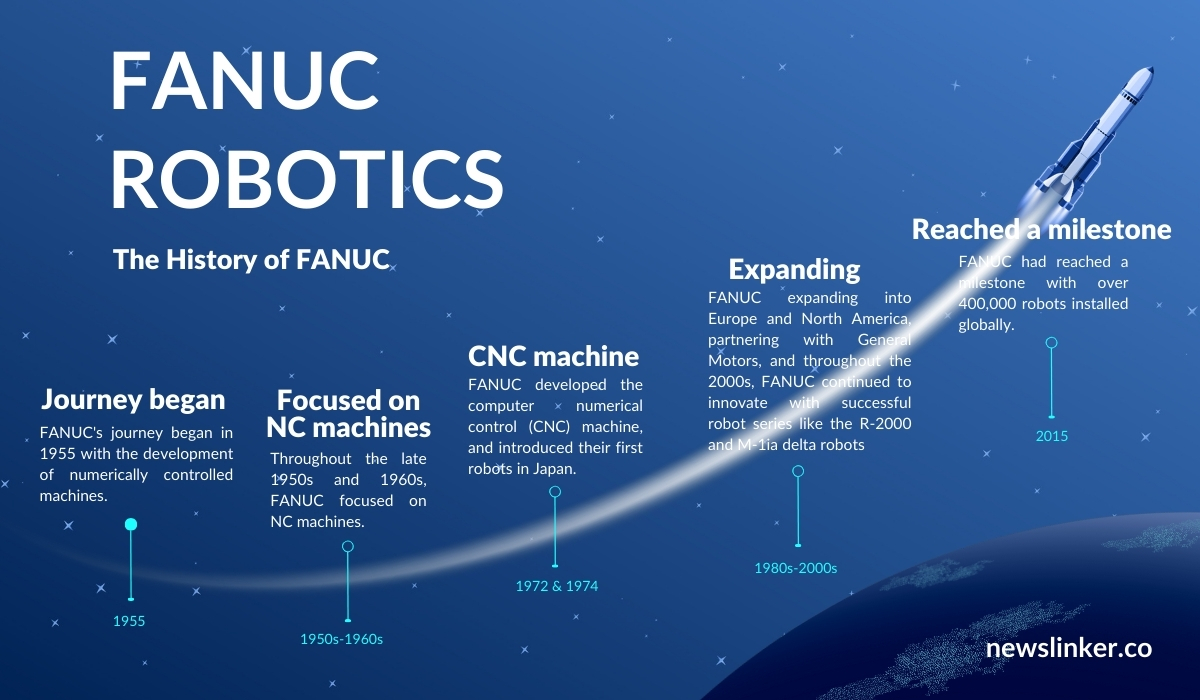
FANUC’s journey began in 1956 with the development of numerically controlled machines. The name FANUC stands for Fuji Automatic Numerical Control. Throughout the late 1950s and 1960s, FANUC focused on NC machines. In 1972, FANUC developed the computer numerical control (CNC) machine, and by 1974, they introduced their first robots in Japan. The 1980s saw FANUC expanding into Europe and North America, partnering with General Motors to form the GMFANUC Robotics Corporation. This partnership marked the beginning of FANUC’s dominance in the robotics industry. Throughout the 2000s, FANUC continued to innovate with successful robot series like the R-2000 and M-1ia delta robots. By 2015, FANUC had reached a milestone with over 400,000 robots installed globally. In 2018, FANUC Academy and FANUC Advanced Researh Laboratory was established and New Yagoya Service Center was opened.
What Does FANUC Stand For?
FANUC stands for Fuji Automatic Numerical Control. This name reflects the company’s origins and its focus on developing advanced numerical control systems for automation.
What Program Do FANUC Robots Use?
FANUC robots use a proprietary programming language called KAREL, designed specifically for robotic applications. Additionally, they use the TP (Teach Pendant) programming language for standard operations. FANUC also offers simulation software called Roboguide for offline programming. The advanced R-30iB controller allows for precise and responsive motion control, supporting complex tasks like path planning and collision avoidance.
How Much Does a FANUC Robot Cost?
The cost of a FANUC robot varies depending on its size, capabilities, and additional features. Prices can range from $25,000 for simpler models like the M1iA, to over $400,000 for heavy-duty models like the M2000/1200. Collaborative robots and specialized robots for food-grade or harsh environments typically have higher costs. A comprehensive robotic system‘s total cost includes the robot itself, controllers, integration equipment, and other components, averaging about 25% of the total system cost.
What Do FANUC Robots Do?
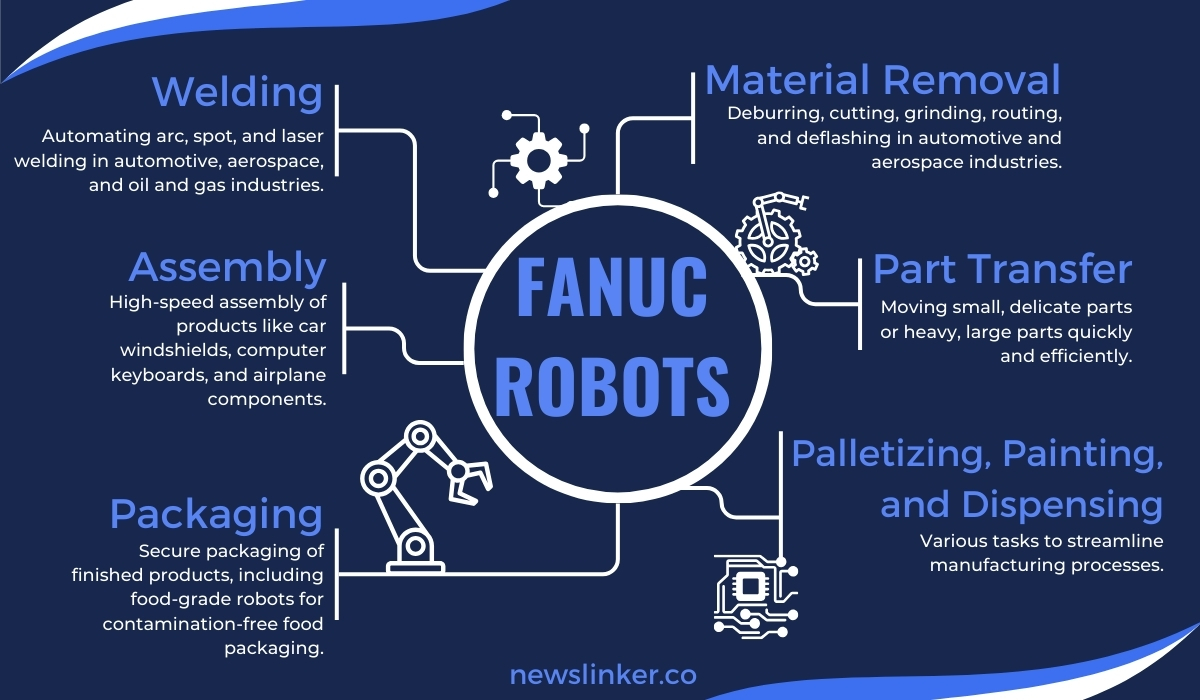
FANUC robots perform a wide range of tasks that include:
- Welding: Automating arc, spot, and laser welding in automotive, aerospace, and oil and gas industries.
- Assembly: High-speed assembly of products like car windshields, computer keyboards, and airplane components.
- Packaging: Secure packaging of finished products, including food-grade robots for contamination-free food packaging.
- Material Removal: Deburring, cutting, grinding, routing, and deflashing in automotive and aerospace industries.
- Part Transfer: Moving small, delicate parts or heavy, large parts quickly and efficiently.
- Inspection and Machine Tending: Ensuring quality control and assisting in machine operations.
- Palletizing, Painting, and Dispensing: Various tasks to streamline manufacturing processes.
What Are the Advantages of FANUC?
FANUC robots offer several advantages. Faster Cycle Times: Robots operate at higher speeds than human workers, increasing throughput and reducing production time. Reduced Costs: Automation reduces labor costs, material wastage, and utility expenses. Precision and Accuracy: Robots are programmed for high precision, ensuring consistent quality and reducing errors. Flexibility: FANUC robots can be reprogrammed for different tasks, providing adaptability in manufacturing processes. Safety: Advanced safety features like collision detection and emergency stops ensure safe operation around humans.
How Does FANUC Make Money?
FANUC makes money through the sale of its robots, automation systems, and related services. The company offers a range of products, including industrial robots, CNC systems, and robotic software. FANUC also generates revenue from maintenance, training, and support services, ensuring long-term relationships with its customers.
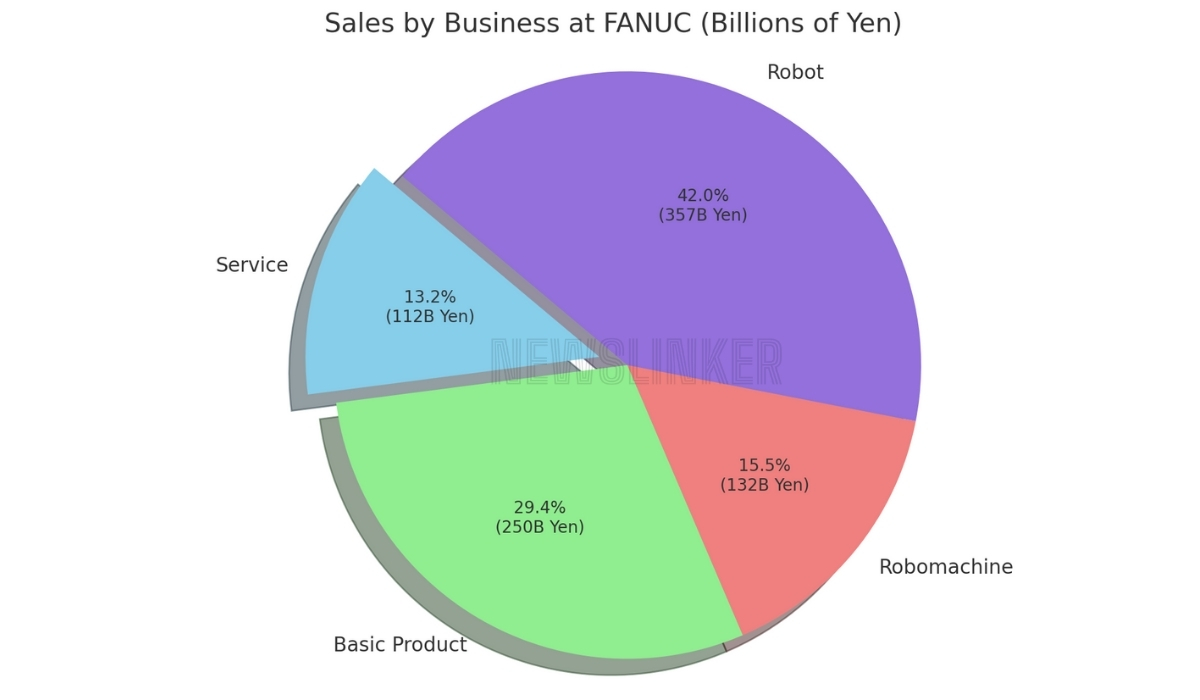
The pie chart provides a detailed breakdown of FANUC’s sales for 2023 by business segment, expressed in billions of yen. The largest segment is Robot, which accounts for 357 billion yen, representing 44.6% of the total sales. This is followed by the Basic Product segment with 250 billion yen (31.2%), the Robomachine segment with 132 billion yen (16.5%), and the Service segment with 112 billion yen (14.0%). Each segment’s contribution is clearly marked with both the percentage and the actual sales figures, offering a clear and comprehensive view of the relative performance and importance of each business area within FANUC’s overall sales strategy. The chart visually emphasizes the dominant role of the Robot segment in FANUC’s business portfolio.
Who Buys FANUC Robots?
FANUC’s customers span various industries, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and logistics. Major automobile manufacturers, electronics producers, and large-scale industrial companies are among FANUC’s primary clients. These businesses invest in FANUC robots to enhance their manufacturing processes, improve efficiency, and maintain high standards of quality.
FANUC Financial Performance
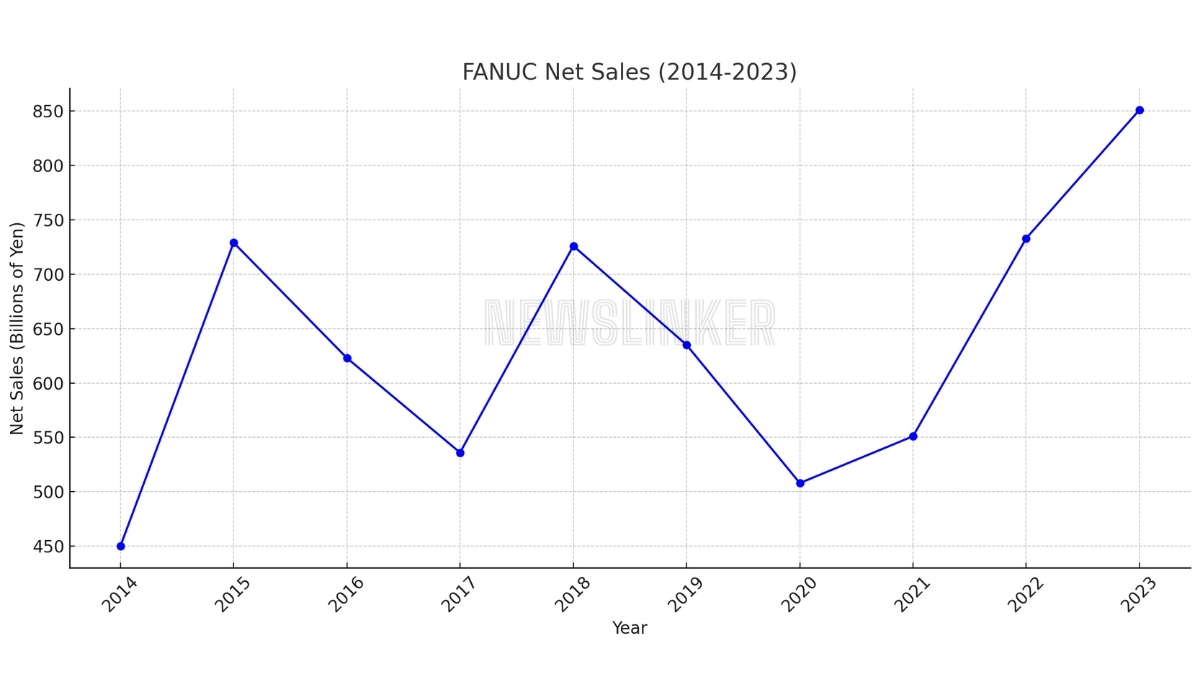
The line chart illustrates FANUC’s net sales from 2014 to 2023, expressed in billions of yen. Over this period, there is a noticeable fluctuation in net sales, with a significant dip in 2017 followed by a recovery. The highest sales were recorded in 2023 at 851 billion yen, indicating robust growth. The sharp increase between 2021 and 2023 highlights a positive trend in FANUC’s financial performance, potentially driven by strategic business initiatives and market demand. This chart effectively showcases the company’s resilience and ability to bounce back from economic challenges.
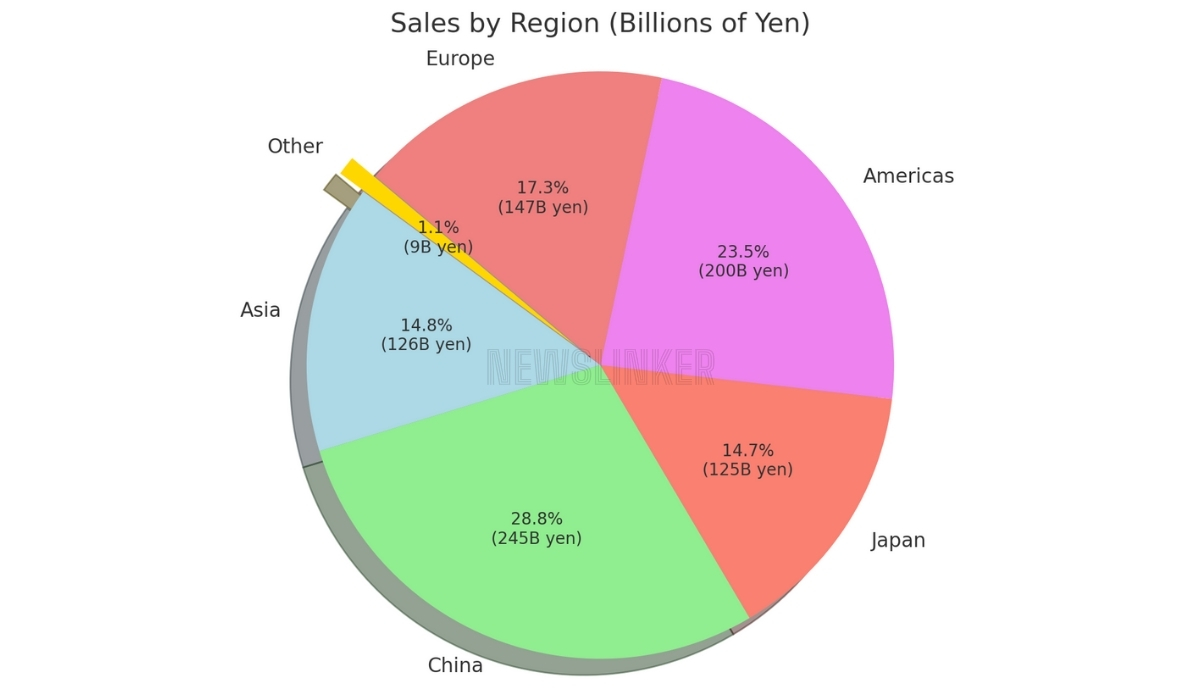
 The pie chart below shows the breakdown of FANUC’s sales, expressed in billions of yen, by region. The chart includes both percentage and actual sales figures for each region, providing a clear view of the sales contributions from different geographical regions. The data shows that China leads with 245 billion yen (44.8%), followed by the Americas with 200 billion yen (36.6%), Europe with 147 billion yen (14.1%), Asia with 126 billion yen (9.6%), Japan with 125 billion yen (9.5%) and Other regions with 9 billion yen (1.6%). This visualization highlights the important role of China and the Americas in FANUC’s regional sales distribution.
The pie chart below shows the breakdown of FANUC’s sales, expressed in billions of yen, by region. The chart includes both percentage and actual sales figures for each region, providing a clear view of the sales contributions from different geographical regions. The data shows that China leads with 245 billion yen (44.8%), followed by the Americas with 200 billion yen (36.6%), Europe with 147 billion yen (14.1%), Asia with 126 billion yen (9.6%), Japan with 125 billion yen (9.5%) and Other regions with 9 billion yen (1.6%). This visualization highlights the important role of China and the Americas in FANUC’s regional sales distribution.
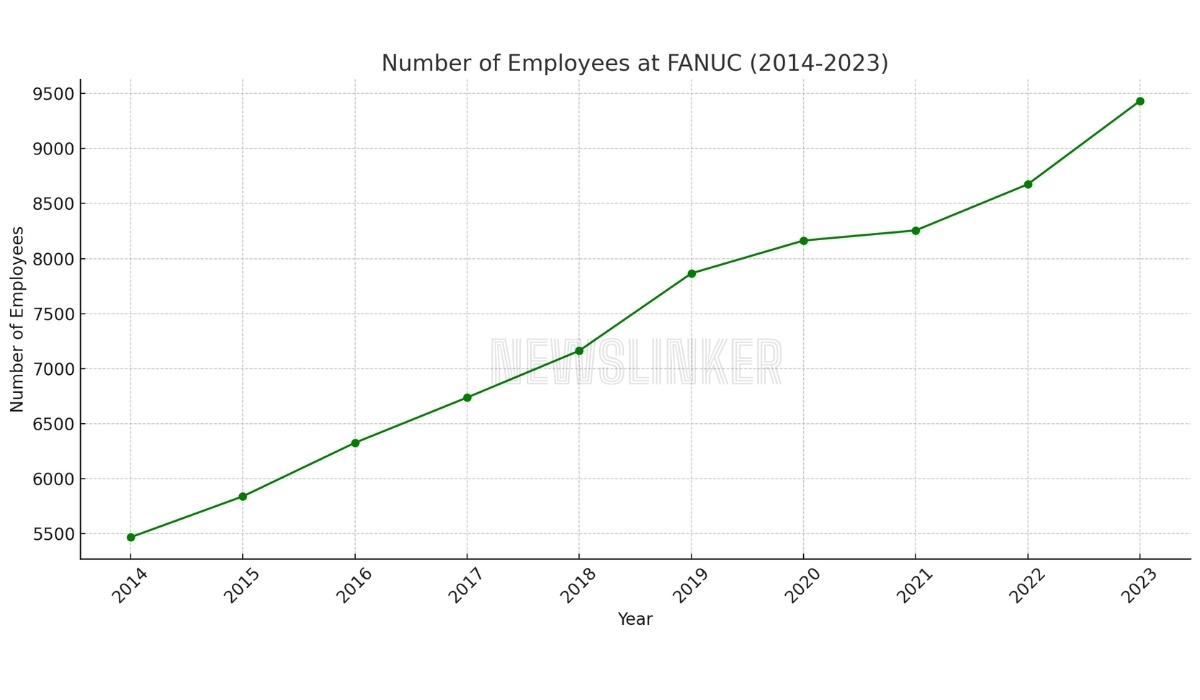
Number of FANUC Employees
The line chart illustrates the number of employees at FANUC from 2014 to 2023. Over this period, there is a clear upward trend in the workforce size, with the number of employees increasing steadily each year. Starting from 5,469 employees in 2014, the company has grown to employ 9,432 individuals by 2023. This growth reflects FANUC’s expansion and increasing capacity, likely driven by its business growth and technological advancements. By 2023, the number of female employees in FANUC’s total workforce is around 7.7% and the proportion of women in management is 1.1%.
In conclusion, FANUC Robotics stands as a leader in the industrial automation sector, offering advanced robotic solutions that revolutionize manufacturing processes worldwide. With a rich history and innovative technology FANUC continues to drive the future of automation.










