Today, digital security is more important than ever. As cyber attacks, data breaches, and phishing scams become increasingly common, relying solely on passwords is no longer sufficient. This is where Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) comes into play. 2FA is an authentication method that provides an additional layer of security to prevent unauthorized access to online accounts.
How does two-factor authentication work? Why is it so important? Which types are more secure, and how can they be implemented most effectively? In this article, we will explain everything you need to know about 2FA in detail.

What is Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) and Why Is It Necessary?
Two-factor authentication is a security measure that requires users to provide two different verification methods when logging into an account. In traditional single-factor authentication, only a username and password are used. However, when 2FA is enabled, the user must provide an additional security factor. This factor is usually a device the user owns, biometric data, or a one-time code.
With this extra security measure, an attacker cannot gain access to an account just by obtaining the password. Passwords can be stolen through phishing attacks, data breaches, keylogger software, and brute force attacks. However, when 2FA is enabled, knowing the password is not enough; the attacker must also have access to the second verification method. This significantly enhances account security.
For example, imagine accessing your bank account not just with a password but also requiring a verification code or fingerprint authentication. This additional security step makes it much harder for attackers and significantly increases account protection.

Types of Two-Factor Authentication: Which Method Should You Choose?
2FA can be implemented in various ways, each with different advantages and disadvantages. Here are the most common two-factor authentication methods:
SMS-Based Authentication
In this method, a one-time password (OTP) is sent to the registered phone number when you attempt to log in. You enter this code to gain access to your account.
- Advantages: Easy to use and widely supported.
- Disadvantages: Vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks and message interception.
Authentication Apps (Authenticator Apps)
Apps such as Google Authenticator, Microsoft Authenticator, and Authy generate time-based one-time passcodes (TOTP) at regular intervals. The user enters the code generated by the app to verify their identity.
- Advantages: More secure than SMS, works offline, and is resistant to SIM attacks.
- Disadvantages: If the phone is lost or the app is deleted, account access can be difficult without backup codes.
Physical Security Keys
Devices like YubiKey and Google Titan Key provide authentication by being plugged into a computer or tapped on a smartphone via NFC.
- Advantages: One of the most secure 2FA methods; highly effective against phishing attacks.
- Disadvantages: Requires carrying an additional device and may not be supported by all platforms.
Biometric Authentication
This method uses biometric data such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or retina scanning for authentication.
- Advantages: Fast and user-friendly, eliminates the need to remember passwords.
- Disadvantages: Limited to supported devices, and stolen biometric data cannot be changed.
Users should choose the most suitable 2FA method based on their needs and security priorities. Authentication apps and physical security keys are considered the best options in terms of security.

How to Enable 2FA on Popular Platforms?
Most major platforms support two-factor authentication to help users secure their accounts. Here’s how to enable 2FA on some of the most commonly used services:
Google (Gmail, YouTube, Drive, etc.): Go to Google Account Settings. Find and enable “Two-Step Verification.” Choose from SMS, an authentication app, or a security key.
Facebook: Log into your Facebook account and go to “Settings & Privacy.” Open the “Security and Login” section. Enable the “Two-Factor Authentication” option.
Microsoft (Outlook, OneDrive, Xbox): Go to Microsoft Security Settings. Enable “Two-Step Verification.”Choose your preferred authentication method.

What is the worldwide adoption rate of dual factor verification security by year?
According to https://expertinsights.com/, the worldwide rates of two-factor authentication security are as follows:
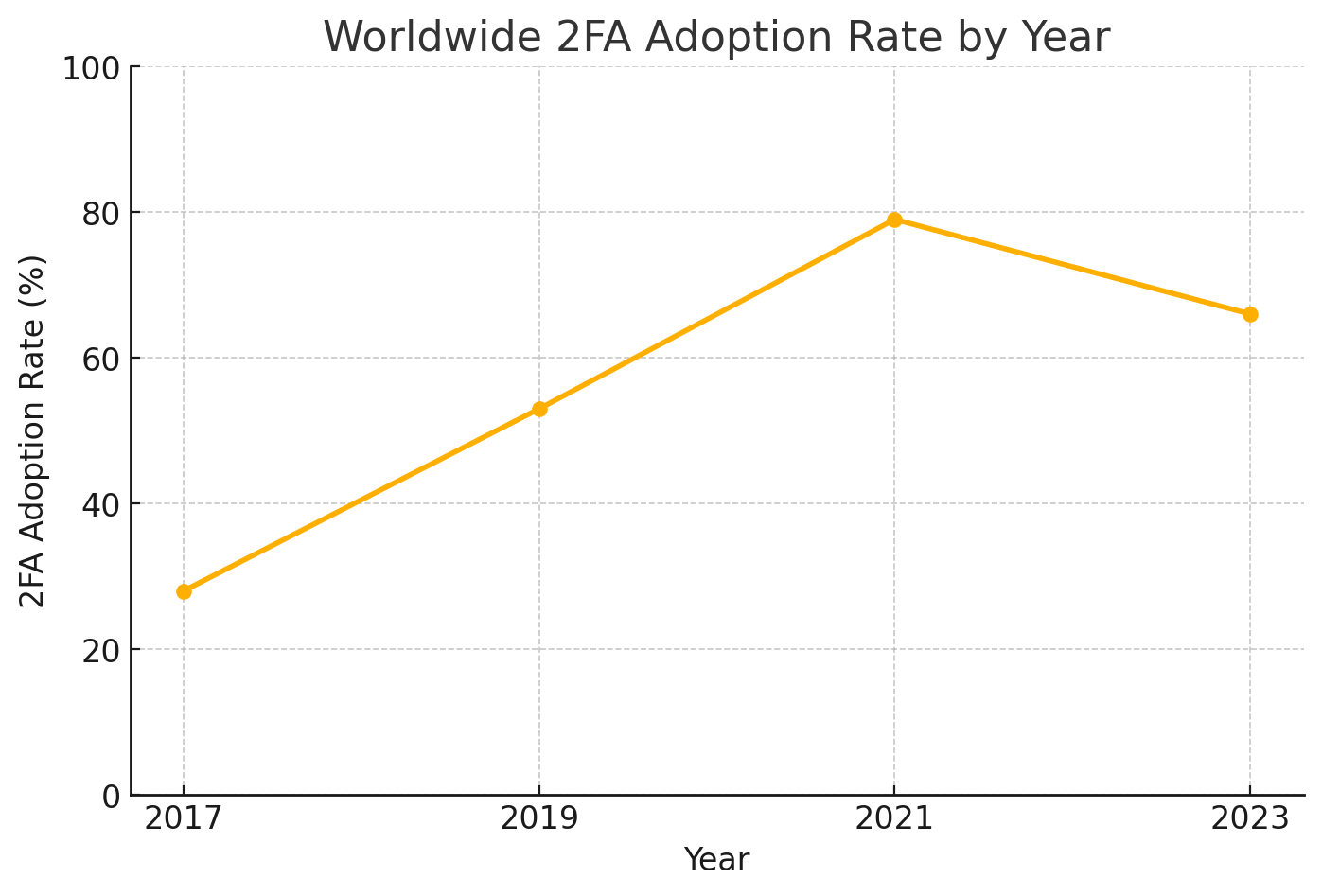
As of 2023, nearly two-thirds of users use multi-factor authentication (MFA). Adoption is higher in large organizations, with 87% of companies over 10,000 employees implementing MFA, while smaller businesses (26-100 employees) have a lower rate of 34%. However, challenges remain; for instance, only 2.5% of Twitter users had enabled 2FA in 2021. While adoption is increasing, there is still significant room for growth, especially among smaller organizations and individuals.
Common Mistakes When Using 2FA and How to Avoid Them
Although 2FA significantly improves security, improper use can introduce risks. Here are the most common mistakes and how to avoid them:
- Not Saving Backup Codes: If the phone is lost or the app is deleted, accessing accounts can be difficult without backup codes.
- Using Only SMS for Authentication: Since SMS has security vulnerabilities, a more secure method (such as authentication apps or physical security keys) should be used.
- Failing to Update Account Recovery Methods: When enabling 2FA, it is important to set up an alternative recovery method, such as a backup email or trusted contacts, for emergencies.
How Will Authentication Evolve in the Future?
In the field of digital security, passwordless authentication methods are becoming more common. Technologies such as passkeys, FIDO2-based authentication methods, and behavioral biometrics may significantly reduce password usage in the future.
In conclusion, two-factor authentication is one of the most effective ways to enhance account security. In today’s world, where cyber threats are increasing, enabling 2FA adds an extra layer of protection to your accounts. To safeguard your digital assets, take action now!











