USB (Universal Serial Bus) has become an indispensable part of modern technology, seamlessly enabling data transfer and powering devices across a wide array of applications. Despite its universal name, USB ports are not created equally. They differ significantly in speed, power delivery, and physical design. This article delves into the evolution of USB technology, the key differences between USB types, tips for identifying them on your devices, and what the future holds for USB advancements.
The Evolution of USB Ports: From Humble Beginnings to High-Speed Connectivity
Since its introduction in 1996, USB technology has undergone a remarkable transformation. The earliest versions, USB 1.0 and 1.1, were designed to simplify the connection of peripheral devices like keyboards, mice, and printers. They offered a modest data transfer rate of up to 12 Mbps, which was sufficient for the limited needs of that era. However, as digital devices evolved and file sizes grew, the demand for faster data transfer speeds led to significant improvements.
In 2000, USB 2.0 marked a major milestone, boosting speeds to 480 Mbps. This advancement not only improved data transfer rates but also enhanced power management, making it suitable for external storage devices, flash drives, and a broader range of peripherals. Its widespread adoption cemented USB as the go-to interface for countless devices.
With the launch of USB 3.0 in 2008, the term “SuperSpeed USB” became synonymous with performance. Offering speeds up to 5 Gbps, USB 3.0 catered to data-intensive applications like SSDs, high-resolution media transfers, and large backups. Subsequent versions, USB 3.1 and USB 3.2, pushed these boundaries even further, reaching 10 Gbps and 20 Gbps, respectively. These iterations also improved power delivery, allowing for more efficient charging and better support for power-hungry devices.
The introduction of USB-C in 2014 revolutionized the USB landscape. Its sleek, reversible design eliminated the frustration of “plugging in the wrong way” and provided unparalleled versatility. Capable of handling data transfer speeds up to 40 Gbps and delivering up to 100W of power, USB-C quickly became the standard for modern smartphones, laptops, and tablets.
Today, USB4, introduced in 2019, represents the pinnacle of USB innovation. By integrating Thunderbolt 3 technology, USB4 supports even faster data transfer rates, up to 40 Gbps, and offers robust capabilities like multiple display support, dynamic bandwidth allocation, and compatibility with a wide range of devices.

Key Differences Between USB Types: Beyond Just Speed
The differences between USB versions go beyond simple data transfer rates. They encompass power delivery capabilities, physical design, and compatibility. Understanding these distinctions can help you make informed decisions when choosing cables, ports, and devices.
Data Transfer Speeds: While early USB versions were adequate for basic tasks, the growing demand for high-definition media, large file transfers, and cloud backups necessitated faster standards. USB 2.0, with its 480 Mbps speed, may still suffice for keyboards, mice, and simple peripherals, but for external hard drives, SSDs, and high-resolution video devices, USB 3.0 and above are essential. USB 3.1 and 3.2 offer speeds up to 10 Gbps and 20 Gbps, while USB4 reaches up to 40 Gbps, making it ideal for professional workflows like 4K video editing and rapid data backups.
Power Delivery Capabilities: Another critical evolution in USB technology is its ability to deliver power. USB 2.0 provides up to 2.5 watts (5V, 0.5A), sufficient for small peripherals. USB 3.0 increased this to 4.5 watts (5V, 0.9A), enabling faster charging for devices like smartphones. However, the introduction of USB Power Delivery (USB PD), especially with USB-C connectors, was a game-changer. This technology supports power levels up to 100 watts, allowing laptops, monitors, and even some compact desktop computers to be powered entirely via a USB-C connection. The future promises even higher power delivery capacities, with some standards supporting up to 240 watts.
Physical Design and Compatibility: USB connectors come in various shapes and sizes, each tailored to specific devices and use cases. USB-A, the most familiar type, is the rectangular connector commonly found on computers and chargers. USB-B is bulkier, often used for printers and external hard drives. Smaller connectors like Micro-USB were once the standard for smartphones before USB-C took over.
The advent of USB-C introduced a sleek, oval-shaped, reversible design that supports both data and power transmission. Unlike older connectors, USB-C is not limited to specific devices—it’s versatile enough for smartphones, tablets, laptops, and even high-performance peripherals like external GPUs and docking stations.

Global USB Devices Market Growth Rates
Global USB Devices Market Growth Rates according to https://www.researchnester.com/:
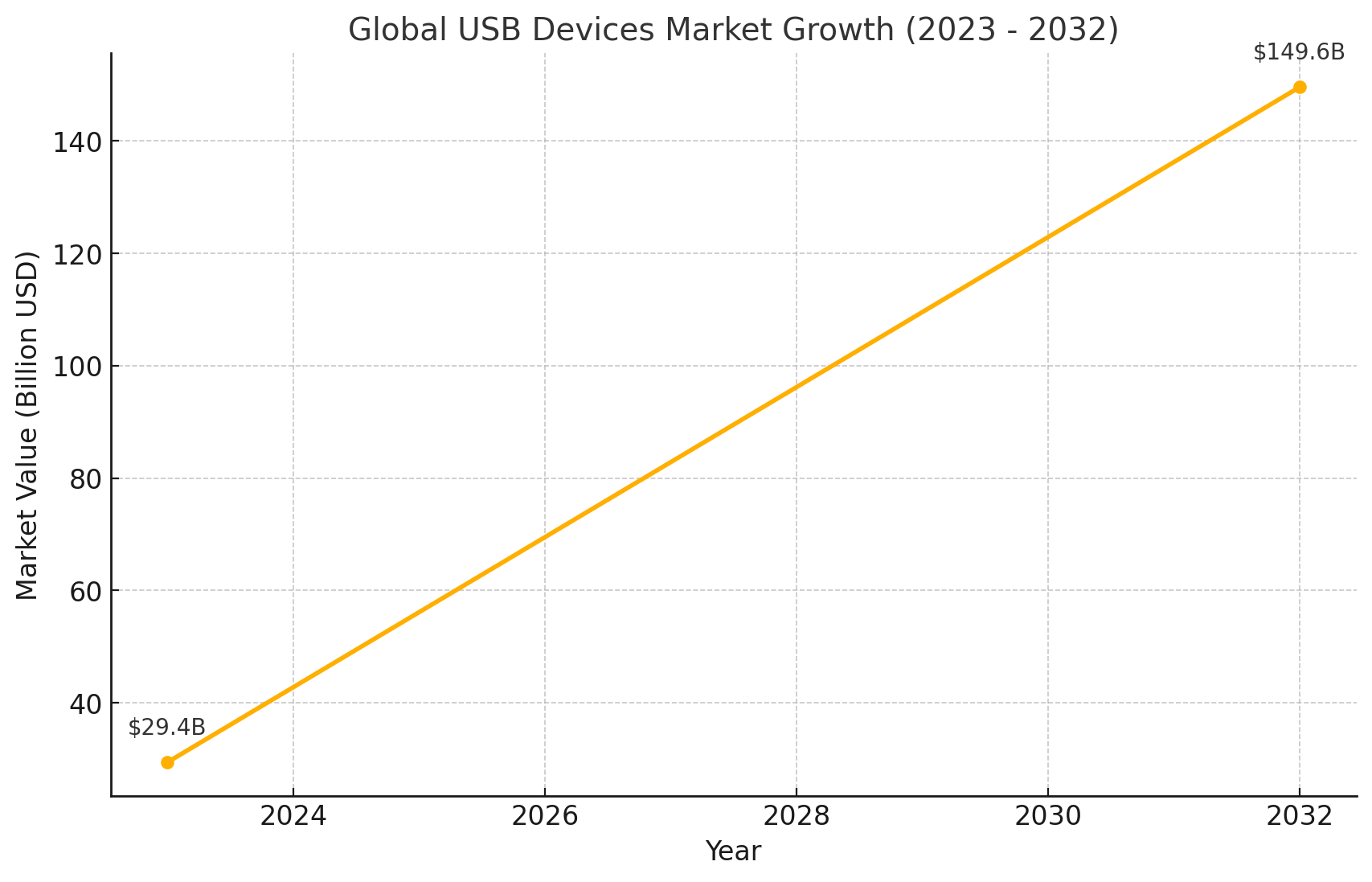
Here is the graph showing the projected growth of the global USB devices market from 2023 to 2032. The market is expected to increase from USD 29.4 billion in 2023 to USD 149.6 billion in 2032, reflecting a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.8%.
Identifying USB Ports: A Visual and Symbolic Guide
Recognizing the different USB ports on your devices can save you from frustratingly slow data transfers or inefficient charging. Here’s how you can identify them:
Color Coding: Many manufacturers use color codes to indicate the type and speed of USB ports:
- White: Indicates USB 1.0 or 1.1 ports, now largely obsolete.
- Black: Typically denotes USB 2.0, offering basic data transfer speeds.
- Blue: Signifies USB 3.0 (SuperSpeed), suitable for faster data transfers.
- Teal: Represents USB 3.1 Gen 2, supporting speeds up to 10 Gbps.
- Red/Yellow: Often used for ports that support high-power charging or “always-on” charging capabilities, even when the device is off.
Symbols and Markings: In addition to colors, ports may feature specific symbols:
- “SS” (SuperSpeed): Indicates USB 3.0 or higher.
- Lightning Bolt Icon: Denotes fast-charging capabilities or high-power delivery.
- Numerical Markings (10, 20, 40): Refer to maximum data speeds in Gbps, corresponding to USB 3.1, 3.2, and USB4, respectively.
Physical Characteristics: The shape and design of the port itself offer clues:
- USB-A: Flat, rectangular, non-reversible.
- USB-B: Square-shaped with beveled edges, used in older peripherals.
- Micro-USB: Small, trapezoidal, commonly found on older mobile devices.
- USB-C: Slim, oval, and symmetrical, allowing for reversible connections.
Choosing the Right USB: Matching Needs with Technology
Selecting the appropriate USB type depends on your specific requirements. For simple peripherals like keyboards and mice, USB 2.0 is adequate. However, when dealing with large file transfers, external SSDs, or high-resolution media devices, opting for USB 3.0 or higher ensures optimal performance.
Modern devices increasingly rely on USB-C due to its superior data speeds, efficient power delivery, and universal compatibility. Whether you’re fast-charging a smartphone, connecting a high-resolution display, or transferring massive files, USB-C—with support for Power Delivery and Thunderbolt—is the go-to choice.
Avoiding Common USB Mistakes
Despite USB’s user-friendly nature, several common mistakes can hinder performance or even damage devices:
- Mismatched Cables: Using a USB 2.0 cable with a USB 3.0 device can bottleneck data speeds.
- Forcing Connections: Non-reversible connectors like USB-A or Micro-USB can be damaged if inserted incorrectly.
- Overloading Power: Connecting power-hungry devices to low-power USB 2.0 ports may cause charging failures.
- Ignoring Port Labels: Overlooking port symbols can lead to missed opportunities for faster speeds or higher power delivery.
The Future of USB: What’s Beyond USB-C?
As technology continues to evolve, so does USB. USB4 represents the latest leap, merging the best of USB-C and Thunderbolt 3 to deliver faster data rates, improved power delivery, and universal compatibility. Future USB developments are poised to support even higher power levels—up to 240 watts—making it feasible to power high-performance laptops, monitors, and more through a single cable.
With global initiatives pushing for universal charging standards, USB-C is set to become the default connector across industries, reducing electronic waste and simplifying user experiences. Moreover, advancements in USB protocols will likely focus on enhancing security, increasing efficiency, and supporting emerging technologies like augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR).
Understanding the nuances of USB ports—how they differ in speed, power, and design—can greatly enhance your tech experience. Whether you’re transferring data, charging devices, or setting up complex workstations, knowing how to identify and choose the right USB type ensures efficiency, reliability, and optimal performance. As USB technology continues to evolve, staying informed about new standards like USB4 will help you make the most of your devices and prepare for the next generation of connectivity.
Device Brands Integrating USB Technology
Many major technology companies incorporate USB ports into their devices and integrate this technology into their ecosystems:
- Apple: Uses USB-C and Thunderbolt 3/4, especially in MacBooks.
- Dell: Produces laptops equipped with USB-C and USB4 ports.
- HP: Offers devices with USB-A, USB-C, and Thunderbolt support.
- Lenovo: Manufactures a wide range of laptops and desktops with various USB ports.
- Samsung & Huawei: Produce smartphones and tablets equipped with USB-C ports.












