Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), often termed as strong or general AI, represents a hypothetical form of artificial intelligence that mirrors human cognitive abilities. Unlike narrow AI, which excels in specific tasks, AGI is envisioned to autonomously learn and perform a wide array of intellectual tasks across different domains, similar to a human. Companies like OpenAI, DeepMind, and Anthropic are at the forefront of AGI research, aiming to create systems that surpass human capabilities in most economically valuable tasks.
The concept, a staple in science fiction, ranges from dystopian narratives of AI dominance to utopian views of AI as benevolent guardians. While AGI remains theoretical, its potential development timeline is debated, with some predicting its arrival within decades and others doubting its feasibility. Key challenges include imbuing machines with self-awareness and consciousness to solve complex problems adaptively. Controversy also surrounds AGI’s existential implications for humanity, with some viewing it as a significant risk and others as a distant, non-threatening concept.
How Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) Works?
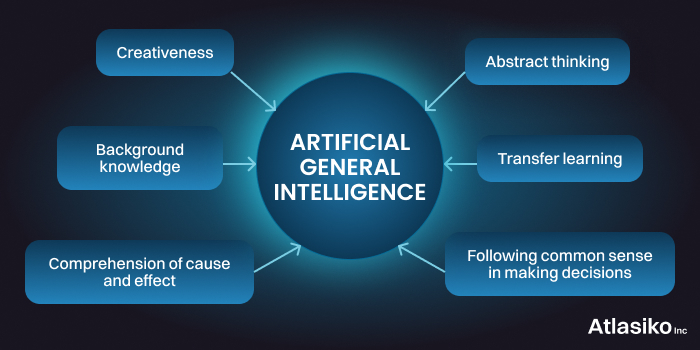
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a theoretical form of AI that aims to replicate the full range of human cognitive abilities in software, enabling it to tackle unfamiliar tasks just like a human. AGI is anticipated to have substantial self-awareness, self-control, and the capacity to learn and solve novel problems beyond its initial programming.
Researchers have not yet reached a consensus on how to achieve AGI, with various proposed methodologies. These include employing neural networks and deep learning techniques, as well as large-scale simulations of the human brain through computational neuroscience. Another approach, the symbolic method, suggests using expanding logic networks to represent human thoughts, enabling AGI systems to process and interpret ideas at a higher level of cognition, similar to human thinking processes. The ultimate goal of AGI is to create systems capable of performing any task that a human can do.
What is the Difference Between AI and Artificial General Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) encompasses a wide range of technologies focused on specific tasks and applications, such as autonomous vehicles or virtual assistants. These systems, often referred to as weak or narrow AI, are powerful but operate within predefined parameters and rely on human-guided training. Conversely, Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), sometimes termed strong AI, remains a theoretical concept aiming to mirror human cognitive abilities.
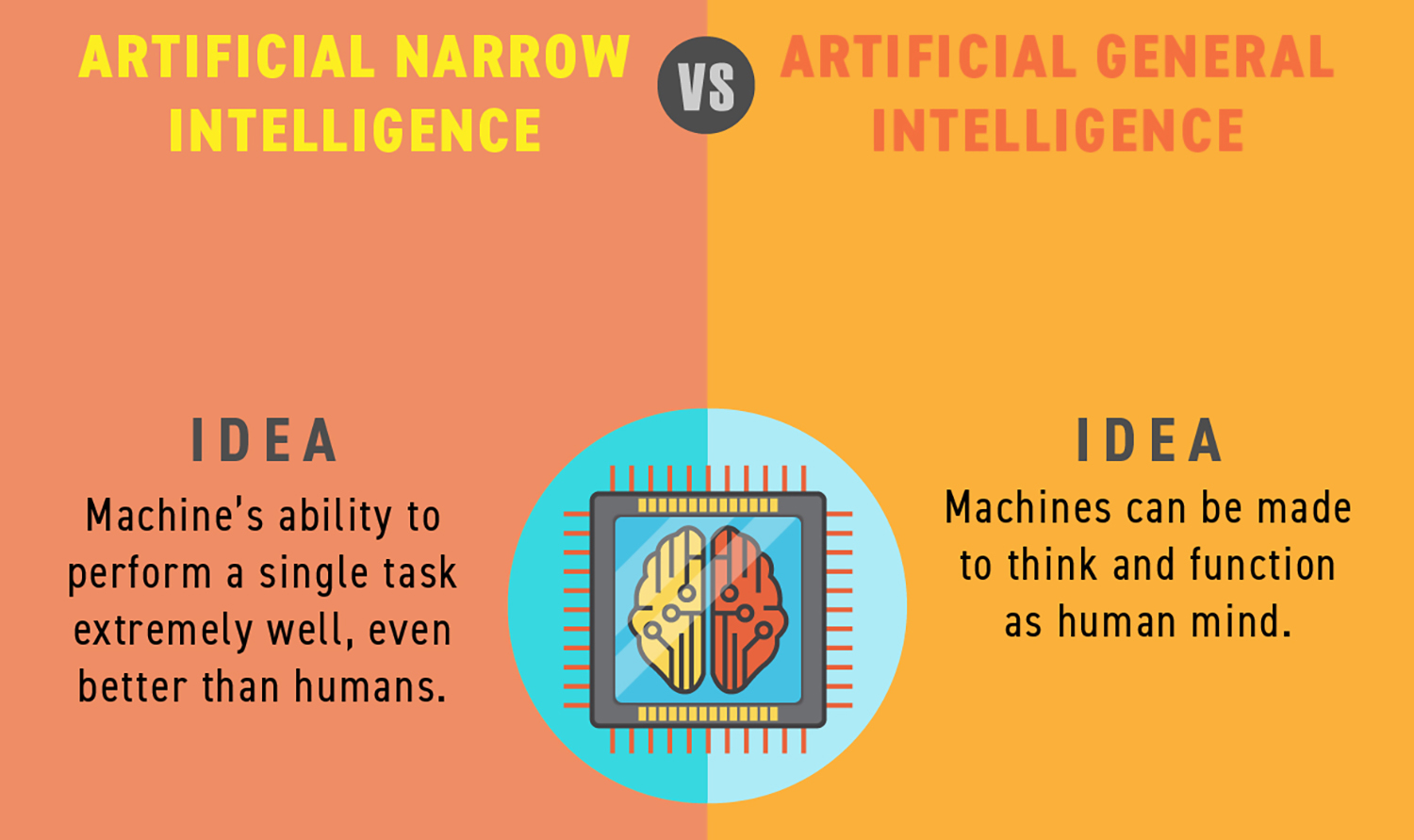
AGI aspires to autonomously solve diverse complex problems across various knowledge domains, matching or surpassing human intellect. Unlike AI, which focuses on specialized tasks, AGI would theoretically be capable of learning and adapting independently, performing any intellectual task a human can. However, AGI’s realization is still debated, with no clear timeline or consensus on its feasibility. While AI is actively employed in various industries, AGI remains a goal for future AI research, representing an advanced level of machine cognition that can autonomously understand, learn, and act like a human being.
Is ChatGPT an Example of AGI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) represent two different stages of AI development. AI, which is widely implemented today, specializes in specific tasks such as voice recognition or autonomous driving, relying on human input for learning and adaptations. Its intelligence, although remarkable, remains less sophisticated than human capabilities. AGI, on the other hand, is a hypothetical, more advanced form of AI that matches or exceeds human cognitive abilities. It’s conceptualized to autonomously solve a variety of complex problems across different domains and learn new tasks without prior programming.

AGI’s development remains theoretical, with debates on its feasibility and ethical implications. ChatGPT, a popular AI model, demonstrates advanced capabilities but is not considered AGI, as it lacks the comprehensive, autonomous learning and problem-solving abilities that define AGI. ChatGPT’s current limitations, such as reliance on dated information and inability to independently acquire new knowledge, distinguish it from the broader concept of AGI. However, advancements in AI like ChatGPT contribute to the foundational work towards the potential realization of AGI.
Is Siri an AGI?

Voice assistants like Siri and Alexa fall under the category of Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), often referred to as weak AI. They excel at specific tasks within a limited scope, such as answering questions, setting timers, or controlling smart home devices like lights. These ANIs are designed for practical functions but lack the broader cognitive abilities associated with Artificial General Intelligence (AGI). In contrast to AGI, which would have the capacity to understand and perform various tasks autonomously across diverse domains, ANIs like Siri and Alexa are tailored for narrow and predefined functionalities. Therefore, Siri is not an example of AGI; it is a prominent instance of ANI.
Examples of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI)
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a complex and evolving concept, with debates surrounding its existence and capabilities. While some researchers argue that AGI has not been fully realized, there are compelling examples of advanced AI systems that exhibit characteristics of AGI.
One notable example is GPT-4, a powerful language model developed by Microsoft in collaboration with OpenAI. GPT-4 is considered by some as an early version of AGI due to its remarkable language mastery and the ability to tackle a wide range of novel and challenging tasks across various domains. These tasks span mathematics, coding, vision, medicine, law, psychology, and more. Importantly, GPT-4 can perform these tasks without requiring specific prompts, showcasing a level of performance that approaches human-like capabilities.
However, it’s essential to note that there is no unanimous consensus regarding AGI. Some, like Sam Altman, the CEO of ChatGPT, argue that models like ChatGPT are still far from achieving true AGI status, emphasizing the need for further development and improvement.










